The healthcare field is undergoing a significant transformation driven by technological advancements. These innovations are reshaping the way patients interact with healthcare providers, access medical services, and manage their health. From telemedicine to artificial intelligence, technology is enhancing the patient experience, making healthcare more efficient, personalized, and accessible.
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring
One of the most notable changes in the healthcare field is the rise of telemedicine. Telemedicine allows patients to consult with healthcare providers remotely, using video conferencing and digital communication tools. This innovation has made healthcare more accessible, particularly for those living in remote areas, patients with mobility issues, and individuals requiring frequent consultations. A study published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research highlights that telemedicine improves patient satisfaction, reduces healthcare costs, and enhances access to services (Dorsey & Topol, 2020).
Remote monitoring devices complement telemedicine by allowing continuous health tracking outside of traditional healthcare settings. Wearable devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers monitor vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels. These devices provide real-time data to both patients and healthcare providers, enabling proactive management of chronic conditions and early detection of potential health issues. According to Grand View Research, the global remote patient monitoring market is expected to reach $117.1 billion by 2025, driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and the need for continuous health monitoring (Grand View Research, 2019).
Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
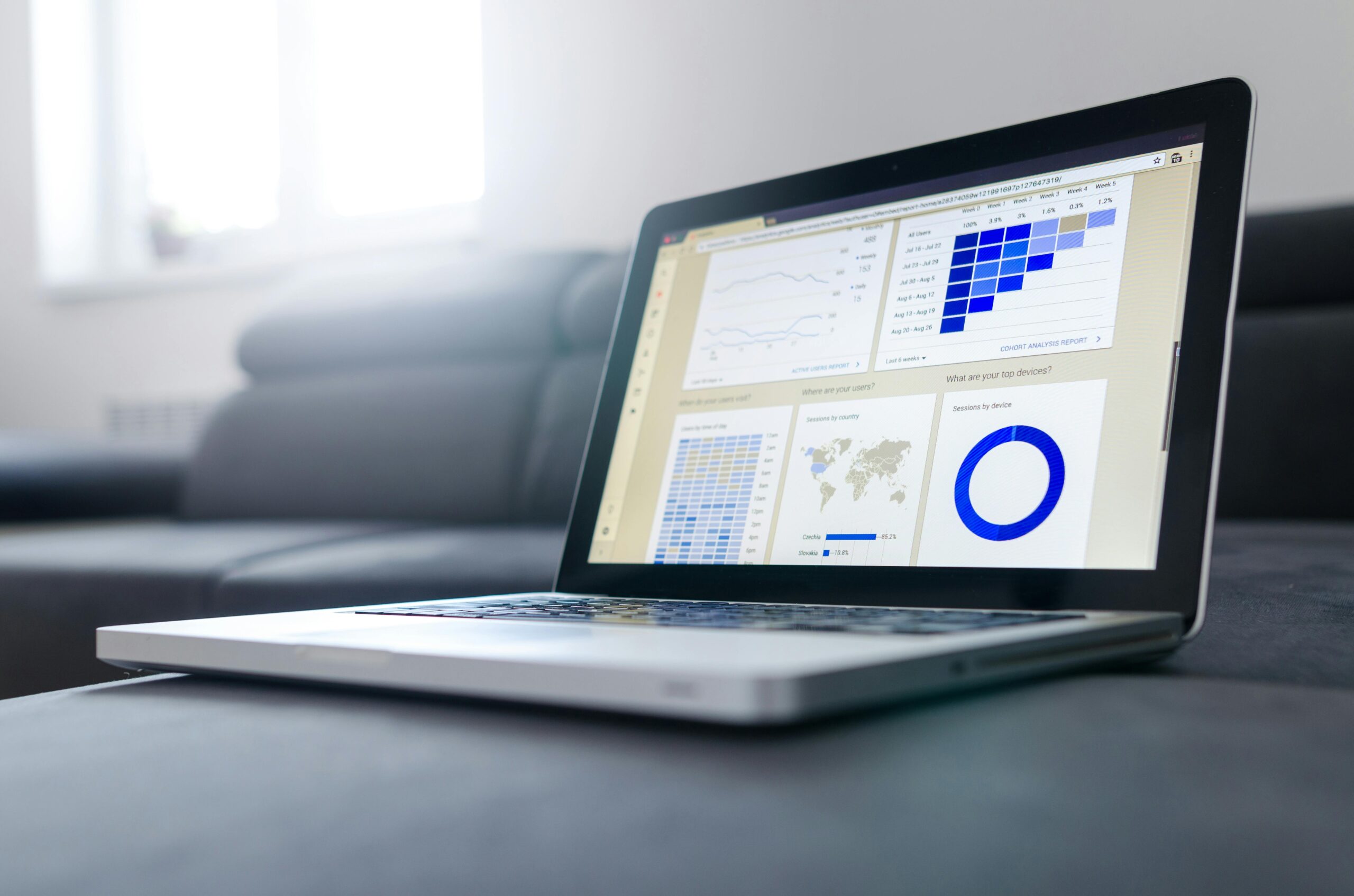
The implementation of Electronic Health Records (EHRs) has revolutionized the management of patient information. EHRs provide a digital version of a patient's paper chart, making it easier for healthcare providers to access and share patient data. This digitalization improves the accuracy of medical records, reduces paperwork, and enhances the coordination of care among different providers. A report by the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) indicates that EHR adoption has led to significant improvements in clinical processes and patient safety (ONC, 2019).
Artificial Intelligence and Data Analytics
Artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics are at the forefront of personalized medicine, offering unprecedented opportunities to enhance patient care. AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of health data to identify patterns and predict patient outcomes, enabling the development of personalized treatment plans. AI-powered diagnostic tools can analyze medical images to detect diseases like cancer at early stages, significantly improving treatment success rates. A review in The Lancet Digital Health found that AI-based diagnostic systems can match or even surpass human performance in various medical tasks, including image analysis and clinical decision-making (Topol, 2019).
Patient Portals and Mobile Health Apps
Patient portals and mobile health apps are empowering patients to take an active role in managing their health. These digital platforms provide patients with access to their health records, appointment scheduling, medication management, and educational resources. By facilitating communication between patients and healthcare providers, these tools enhance patient engagement and self-management of health conditions. A study in the Journal of Medical Internet Research found that patient portals improve patient satisfaction, adherence to treatment plans, and overall health outcomes (Kruse et al., 2017).
Enhancing Patient Experience through Personalized Care
Personalized care, made possible by technological advancements, is becoming the cornerstone of modern healthcare. AI and data analytics enable healthcare providers to tailor treatments and interventions based on individual patient profiles. This approach not only improves patient outcomes but also enhances the overall patient experience by ensuring that care is specifically designed to meet each patient’s unique needs. Moreover, technologies such as virtual reality (VR) are being used to improve patient experiences in areas like pain management, physical therapy, and mental health. VR can provide immersive environments for rehabilitation exercises, distraction during painful procedures, and therapeutic interventions for conditions like anxiety and PTSD.
Conclusion
Technology is undoubtedly transforming the patient experience in healthcare, making it more efficient, personalized, and accessible. Telemedicine and remote monitoring are breaking down geographical barriers to care, while EHRs are improving the accuracy and coordination of patient information. AI and data analytics are paving the way for personalized medicine, and patient portals and mobile apps are empowering patients to take control of their health.
As technology continues to evolve, it will further enhance the patient experience, leading to better health outcomes and a more responsive healthcare system.
References
- Dorsey, E. R., & Topol, E. J. (2020). Telemedicine 2020 and the next decade. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 22(9), e19460. https://doi.org/10.2196/19460
- Grand View Research. (2019). Remote patient monitoring system market size, share, trends analysis report by product, by application, by end use, by region, and segment forecasts, 2020 – 2025. https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/remote-patient-monitoring-system-market
- Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC). (2019). Electronic health records: A systematic review of published studies. https://www.healthit.gov
- Topol, E. J. (2019). High-performance medicine: The convergence of human and artificial intelligence. The Lancet Digital Health, 1(2), e100-e109. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2589-7500(19)30036-0
- Kruse, C. S., Bolton, K., & Freriks, G. (2017). The effect of patient portals on quality outcomes and its implications to meaningful use: A systematic review. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 17(2), e44. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.3171